
Depending on it, AAS is of two types Flame-AAS, and electrothermal or graphite furnace-AAS The atomizers most commonly used nowadays are flames and electrothermal (graphite tube) atomizers.
#Hollow cathode lamp block diagram free
Because the atomic absorption method is largely free of interference and the set of electronic energy levels is specific to that element, it is a highly good analytical technique with great sensitivity. It is used to determine the concentration of metals present in a sample to be analyzed.ĪAS can be used to quantify more than 70 different elements either in solution or solid form and possesses wider applications in clinical analysis, food analysis, the pharmaceutical industry, the mining sector, and so on. Difference between flame photometry and atomic absorption spectroscopyĪtomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) is an absorption spectroscopic method that uses the absorption of light by free atoms in a gaseous state to determine the quantitative composition of chemical components.Disadvantages of atomic absorption spectroscopy.Advantages of atomic absorption spectroscopy.

Application of atomic absorption spectroscopy.Interferences in atomic absorption spectroscopy.Atomic absorption spectroscopy instrumentation.Principle of atomic absorption spectroscopy.(l)Solute-volatilization interference occurs when the rate of volatilization of aerosol particles changes due to the lack or presence of a concomitant. (k)The interfering substance provided in excess to avoid spectral interferences is known as a radiation buffer. (j)Chemical interference is defined as a change in absorption properties or an analyte's emission caused by chemical processes such as atomization. (i)The phenomenon of spectral interference is the overlapping of an analyte's absorption line by another interfering species. (h)The absorbing back of emitted radiation by non-excited atoms in the lamp is referred to as self-absorption. (g)Sputtering is the process of forming atomic clouds in a hollow cathode lamp. (f)A hollow cathode tube is a type of glass tube that is frequently used in atomic absorption studies. (e)Pressure broadening is the process by which the collision of absorbing or emitting species with other ions generates a broadening of spectral lines compared to normal ones.
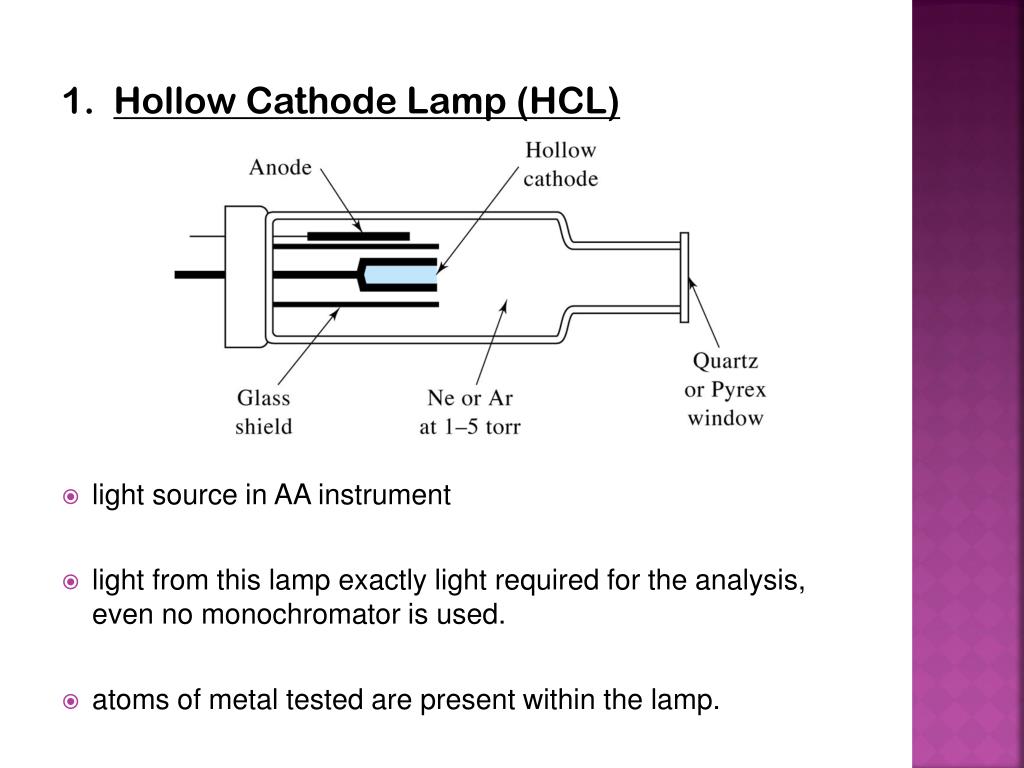
(d)Atomization is the process of converting samples to atoms. (c) The ionization suppressor allows for greater electron concentration to be introduced, which improves sensitivity. (b) In Atomic absorption spectroscopy, protective agents are chemicals that generate stable volatile species and overcome interference. (a)Cations that interact with the analyte and remove chemical interferences are referred to as releasing agents.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
